What is the main cause of air pollution?

Pollutants generated by humans
Human activity generates primary and secondary pollutants. But how are these different? Primary pollutants come straight from sources of pollution such as industry, heating, transport and agriculture. They include nitrogen oxides (NOx), sulphur dioxide (SO2), volatile organic compounds (VOC), hydrocarbons and fine metal particles (lead, cadmium, etc.). Secondary pollutants are created in the atmosphere, as a result of chemical reactions between various pollutants that produce ozone, nitrogen dioxide and ultrafine particles.
Industries responsible for air pollution
How do we generate air pollution?
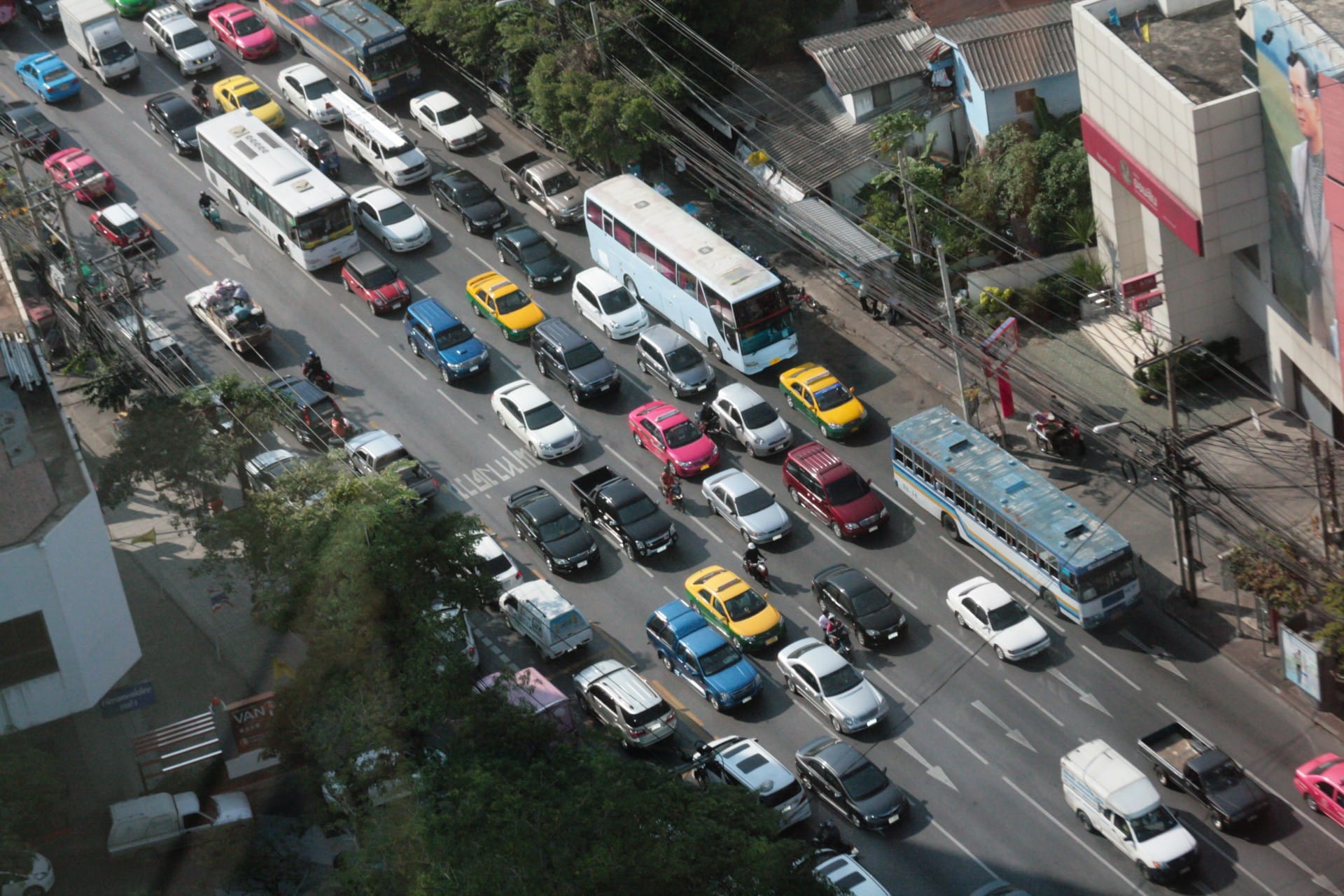
- Leading the pack is the residential sector, especially home heating, and road transport. But it’s not the same up and down France. These activities are therefore respectively responsible for half and a quarter of fine particle emissions in Ile-de-France. Whereas in Haute-Savoie, in the Arve valley, 80% of polluting emissions come from individual wood heating systems.
- Industry also plays a major role in air quality. Factories contribute to pollution with sulphur dioxide (SO2), non-methane volatile organic compounds (VOCnM), PM10 fine particles and even nitrogen oxide (NOx) in France. Airparif estimates that more than 50% of sulphur dioxide pollution in Ile-de-France is generated by industrial activities.
- As for agriculture and forestry, they are not far off as the main sources of air pollution. Spreading, livestock effluents, etc. represent 93% of ammonia production (NH3), 42% of NMVOC emissions, 25% of PM10 emissions and 11% of PM2.5 emissions, according to the SECTEN 2021 report by Citepa.
- Non-road transport methods aren’t all squeaky clean either, especially planes. In addition to the CO2responsible for global warming, aeroplanes generate air pollution with fine particles, especially those related to nitrogen oxides (NOx), contrails, sulphur dioxide (SO2), and carbon particles.
A key public health problem
Air pollution is a major concern for both public health and the environment. We need to understand where it comes from and pinpoint the main sources of air pollution to arm ourselves better in the fight against this scourge that causes at least 40,000 deaths each year in France. But to finish on a positive note: In France, atmospheric pollution emissions are down since 1990 (heavy metals, acidifying and eutrophication pollutants, particles, and persistent organic pollutants).