FAQ

What type of pollution is caused by road traffic?
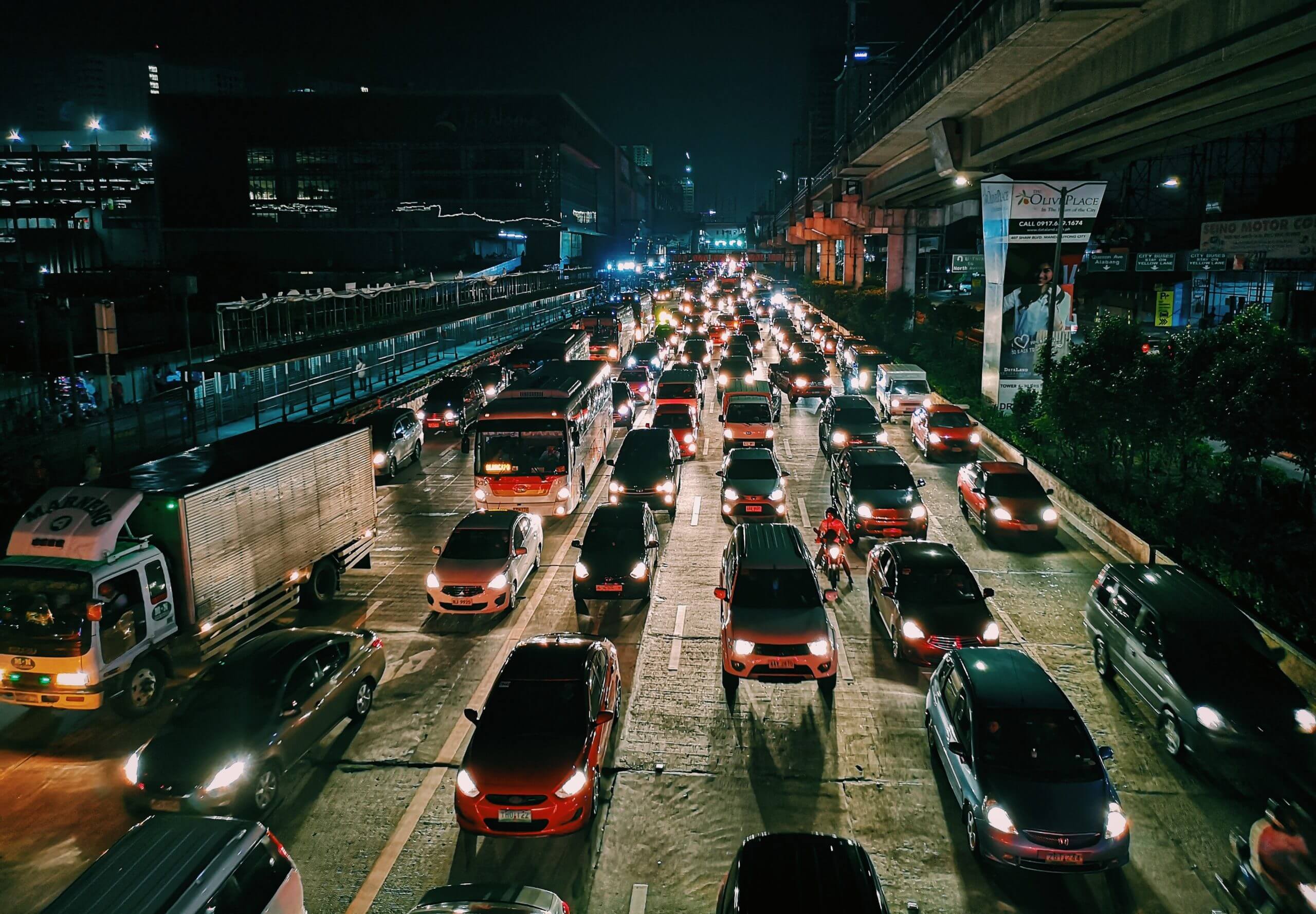
Air pollution exposure causes 40,000 deaths each year in France. How? Road transport comes top on the list of pollutant sources, neck and neck with the residential sector (home heating especially). Pollution is generated by vehicle traffic during chemical and physical reactions:

- Carbon monoxide (CO) is a poisonous gas that escapes when fossil fuel is burned at temperatures that are not quite high enough for full combustion. Oxygen and carbon molecules then join together to form carbon monoxide. When a vehicle starts its engine, it releases a lot of this pollutant into the atmosphere, but the amount varies depending on the vehicle and traffic conditions.
- Another source of pollution associated with traffic is nitrogen oxides (NOX): nitric oxide (NO) and nitrogen dioxide (NO2). Released during the fossil fuel combustion process, these two gases come into contact with water vapour and generate acids that interact with gases and volatile particles to form nitrates and other compounds that are harmful to respiratory health and the environment. They also contribute to acid rain.
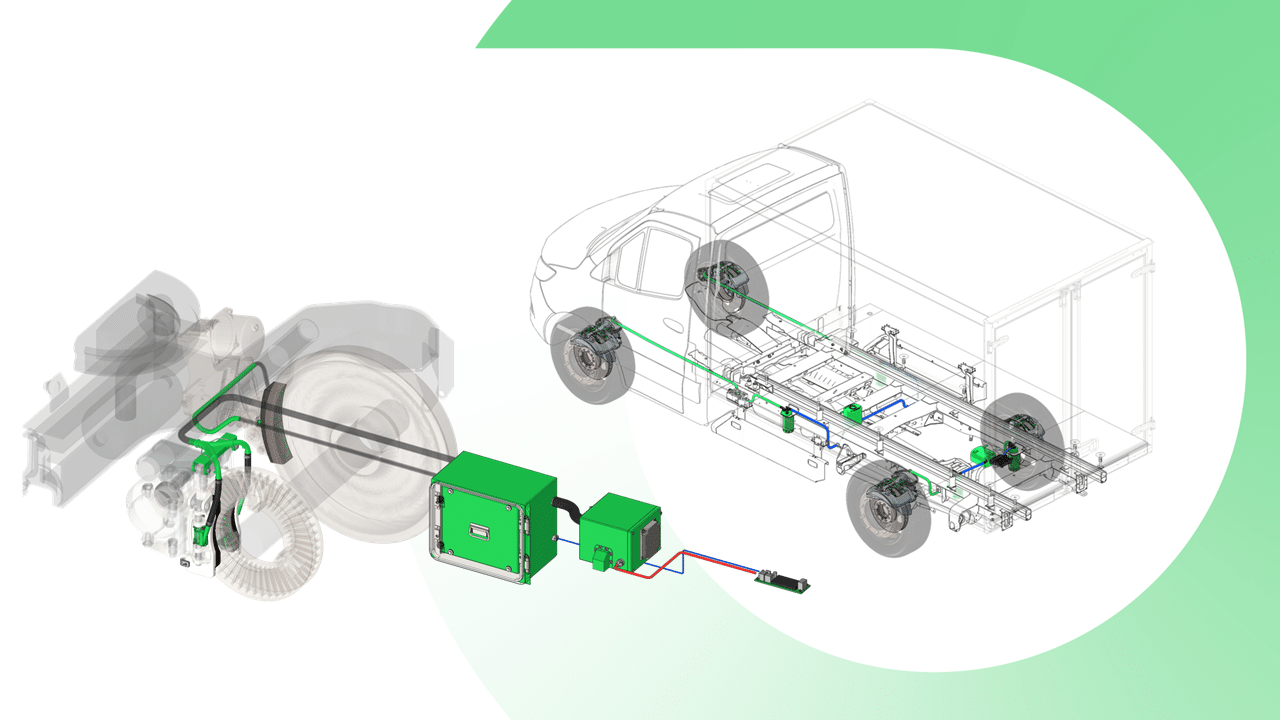
- Fine particles (FP) include those in exhaust fumes that are generated by fuel combustion, and fine friction particles that are a result of tyre and brake wear and tear. Fine particles are complex composites. And unlike the fine particles in exhaust fumes, they do not change their composition on contact with other pollutants in the atmosphere. They are toxic due to their composition, shape and size: the finer the particle, the further it can penetrate inside the body. Unlike other sources of pollution associated with vehicle traffic (CO, NOX, HC, O3, FP from exhaust fumes), fine friction particles are here to stay, even as electric vehicles become more popular. Often underestimated by public policies and regulations, they are a major health risk, causing oxidative stress,* respiratory or cardiovascular disorders, cancers, neurodegenerative diseases (Parkinson, Alzheimer), etc.
- Unburned hydrocarbons (HC) are another source of pollution caused by traffic. They are generated when fuel combustion is incomplete. This mostly happens in poorly maintained engines and when vehicles are filled with low-quality fuels. Unburned hydrocarbons are released in exhaust gases. Made up of carbon (C) and hydrogen (H), the unburned hydrocarbons ejected into the air contribute to the formation of ozone. They are harmful to health and cause anxiety, cardiovascular disease, heart attacks, brain degeneration and an increased risk of cancer.
- Ozone (O3) is a so-called “secondary” pollutant which is not emitted directly by petrol or diesel vehicles but created during the chemical reaction between nitrogen oxides and volatile organic compounds under the effect of heat and sunlight. Its impacts on human health and the environment are serious: asthma, breathing difficulties and an increased risk of stroke.
* Oxidative stress occurs when a cell can no longer manage the excessive presence of toxic molecules, mainly from cellular respiration, free radicals. They can damage cells and DNA.
Discover more questions
Every year in France, air pollution and fine particles cause 40,000 premature deaths. If we’re going to reduce that impact, we need to understand more about them. But behind the generic term “fine particles” lurks a variety of meanings. Fine particles can take different sizes and shapes, can be made up of different things, and can come from different sources. It’s time to take a closer look.
The term “fine particle” refers to an aggregate of polluting chemical compounds created during combustion, friction or chemical reactions. Forest fires, volcanic eruptions, and desert dust: fine particles can occur naturally. But most fine particles are generated by human activity. How? Mainly from road traffic (exhaust gases and abrasion caused by brakes on tyres and the road), home heating, and industrial and agricultural emissions.
As we inhale 15,000 litres of air every day, we are continually exposed to air pollution, especially in large cities. These gases and fine particles are not only harmful to our health, but they also damage the environment and ecosystems and accelerate climate change. Where does air pollution come from? Although pollutants may be of natural origin: pollens, forest fires, sand mists, soil erosion, and volcanic eruptions generate pollution over which we have very little control, human activity is the main source of air pollution. That is evidenced by the sharp decline in air quality from the 19th century, with the development of industry and road traffic.